How IoT, Blockchain & AI has transformed Water Utilities and Industries to accelerate Conservation
Posted by Ganesh Iyer, CTO Knowledge Lens on July 25, 2018

Challenges
Some of the major challenges that Water utility companies face include:
Need to plug Revenue leakages:
Approx. 5-10% of retail utility water is unaccounted and unbilled for. The losses can be in the form of metering inaccuracies, data capturing and reporting errors, unbilled meters, undetected leaks and unauthorized consumption. Utilities can benefit from reocovering this hidden revenue through efficient real time monitoring and detection.
Increasing pressure to meet conservation targets:
There is rising global water stress and subsequently existential risks faced by industries with water-intensive processes such as food and beverage, power, pulp and paper. In addition to this there are regulatory requirements that encourage best practices and innovative solutions for protecting ecosystems, conserving water supplies, and improving water quality. Utilities can play a major part in industrial water conservation by helping industries monitor their water usage, avoiding wastage and promote recycling by less expensive solutions like Zero Liquid Discharge (ZLD) processes.
Lack of clarity in scenario and operational planning:
Utilities have the need to understand revenue profiles, plan strategies, and accurately visualize the impact of new rate structures before ever bringing them to customers. Utilities currently do not have capabilities to include factors like climate conditions, economic scenarios or historic rate revision impacts in their scenario planning.
Improving operational effectiveness:
Utilities typically need their assets (e.g. pumps) to operate at 70% or more capacity consistently. More often, degradation of performance is usually unnoticed, and this leads to money wasted on unplanned downtimes, maintenance cost over-runs and increased energy costs due to sub-optimal operating conditions of assets.
Solution
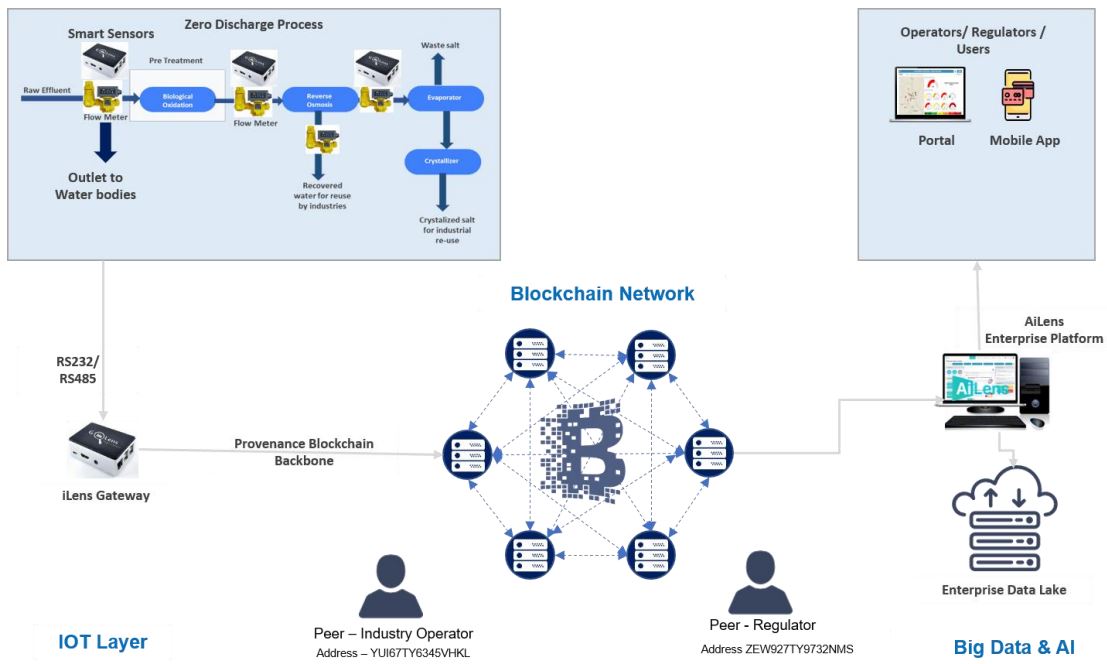
Figure 1 depicts our Solution Overview wherein we have engineered an Industrial Platform using IoT, Blockchain and AI technologies to achieve this transformation.
Our clients in textile dyeing industry as well as power, oil & gas, pharma, pulp & paper, chemical, petrochemicals etc., generate large volumes of waste water with high salinity/TDS that need management. In most cases, these wastewaters are discharged via a plant outlet to a surface water body, an evaporation pond, or in some cases into deep wells. Discharge of saline but treated wastewater pollutes ground and surface waters. There are growing environmental concerns regarding such discharge practices, which has resulted in the development of Zero Liquid Discharge (ZLD) processes. The water should not be released to the water bodies used by the public. Zero liquid discharge which promotes water reuse by the industries themselves. These are achieved through Industrial effluent treatment, sewage reuse and desalination.
Monitoring of water meters at inlet and outlet points of Effluent treatment unit would monitor the flow rate and the total volume of water that is being used in the entire process. For example: if the value of outlet flow meter indicates “0”, then it infers that there has been Zero discharge.
The flow meter data gets transmitted to the blockchain through an IoT Gateway device, which in-turn is transmitted to the Blockchain Provenance backbone. The Regulator and Industry operator are the peers registered on the blockchain network and trust is between them. For any deviation in the flow meter reading, for values greater than 0, which indicates that discharge of water from outlet to water bodies, the contract is violated which leads to Regulator penalizing the Industry. Also, blockchain helps in providing security for IoT Gateway devices through prevention of installation on malicious software on the gateway devices.
The data would then be maintained in an Enterprise Data lake. Once, real-time data is available, cleansed and aggregated, following Artificial Intelligence techniques and feedback optimized models are executed:
Exploratory Statistical Data Analysis to identify median trends of water consumption at the consumer / county (or) industry/industry segment level and provide dashboards to indicate water-consumption against average.
Customer Segmentation Analytics to segment customers into distinct water usage groups.
Correlation Analysis to identify trends related to water consumption across consumer segments (e.g. impact due to number of people in household/weather patterns etc).
Predictive machine learning models using Regression/Random Forest, for identifying water losses across loss categories defined as per AWWA standards.
Simulation Models using Monte-Carlo that will help in Pricing Simulation and Optimization. This will have features to set rate parameters including climate, economic scenarios and effect of surcharge changes.
Predictive deep learning models using TensorFlow to calculate residual life of assets (e.g. Impellers) based on various parameters like pump speed, flow rate, pressure, supply reservoir levels etc.
Other problem statement to address would be, Urban water Management using treatment plants and efficient use of Urban Water distribution. Using flow meters and the above solution to check water consumption at homes and data from them to analyse consumption patterns. If average consumption for a city is pegged at a certain level and if a household consumptions drastically high volumes of water, then there is a provision to investigate for any leakages, awareness on saving water etc.
Benefits and ROI
Industries are immensely have been benefited from our Solution implementation, some of them are listed herewith:
Increased Revenue
o Meter-level identification of various Loss categories per AWWA resulting in top line revenue identification
o Prioritized meter replacement schedules
o Increased Revenue by eliminating meter discrepancies
Conservation & Compliance targets adherence
o Reduced Compliance Risk — Comply with Bill 555, Water Stewardship Act 2010, and similar regulations
Pricing Optimization
o Improved scenario planning by helping CXOs visualize the impact of new rate structures before ever bringing them to customers
o Adjust customer classes and rate structures for increased revenues
Improved Operational Effectiveness
o Better visibility to plant operators by real time alerts (e.g threshold exceedance) and by helping reduce downtime and maintenance costs
o Savings in energy costs
Article credits : Sreesankar, CIO Knowledge Lens, Cariappa, CBO Knowledge Lens on July 25, 2018
